|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Faber T.E. Ч Fluid Dynamics for Physicists |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Acceleration, centripetal 41
Acceleration, representation of 14Ч15 38 40
Acoustic streaming 285Ч8
Adiabatic (as opposed to isothermal) flow 81 6
Adiabatic lapse rate see atmosphere temperature
Aeolian harp 260
Aerofoils, flow past 28 271 274 277
Aerofoils, forces on 115 273Ч8
Aerofoils, shape of 268 271 272 274 276Ч7
Alfv n waves 415 n waves 415
Angular velocity, of fluid 22 200 393
Anisotropic fluids 385 (see also flow alignment; flow birefringence; plasmas; polymeric liquids)
Anti-thixotropy 409
Aspect ratio 308 316
Aspirator, water jet 76
Atmosphere, general circulation of 338Ч9
Atmosphere, temperature gradient in 89Ч90
B nard convection 314Ч22 324Ч8 349Ч51 378Ч83 nard convection 314Ч22 324Ч8 349Ч51 378Ч83
B nard convection, in nematic liquid crystals 412Ч13 nard convection, in nematic liquid crystals 412Ч13
Benjamin Ч Feir instability 341 2
Bentonite gels 408Ч9
BernoulliТs theorem, for potential flow 47Ч8 122Ч3
BernoulliТs theorem, for steady compressible flow of ideal gas 86Ч7
BernoulliТs theorem, for steady flow of Euler fluid 14Ч16 46Ч9
Birefringence see flow birefringence
BordaТs mouthpiece 57
Bores 67Ч72
Bose Ч Einstein condensation 416
Bound vortices 146 147Ч50 270Ч3
Boundary conditions, at fluid-fluid interfaces 166Ч70 175Ч6
Boundary conditions, at fluid-solid interfaces 23Ч5 168Ч9
Boundary layer equations 244
Boundary layers 25Ч9
Boundary layers, at free surface of liquid 29 169
Boundary layers, in convecting fluid 312Ч14 379 381Ч3
Boundary layers, in oscillatory flow 29 141 211Ч12 285Ч6
Boundary layers, on cylinders 252Ч3
Boundary layers, on plates 243Ч51 375Ч8
Boussinesq equations 303Ч5
Brown Ч Roshko vortices 347Ч8
Bubbles, collapse of 54Ч6
Bubbles, effect of ultrasonics on 127
Bubbles, rate of rise of 232 (see also suspensions)
Buffer zone, in turbulent shear flow 372 374Ч5
Bulk viscosity 201 2 236 431 435
Canals, waves in 179Ч80 182Ч6
Capillary waves see ripples
Cavitation 38 54Ч6
Chaos, routes to 344
ChladnyТs plate 287Ч8
Choked flow 90Ч3
Chord, of aerofoil 272
Circulation 120Ч2
Closure problem 346
Co-moving reference frame 39
Coanda effect 73Ч7
Coherent structures, in turbulent flow 347Ч8 369 378 382Ч3
Compressibilities 3 16 79
Compressibilities, of ideal gas 81 2
Compressible flow 17 78Ч118
Computational fluid dynamics, or computer simulation in fluid dynamics see numerical methods
Condensation (in compressible flow of gases) 96
Condition 37Ч8 39 40 120
Conformal mapping 131 161
Conformal transformation see conformal mapping
Constrictions, flow through 81 90Ч3
Contraction coefficient, at 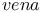 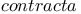 57 63 57 63
Contraction coefficient, for Venturi meter 52
Control volume 71
Convection, thermal see B nard convection; nard convection;
Coriolis force 45 225 339
Couette flow 222Ч4 328Ч31
Creep, in solids 384
Creeping flow 195 228
Curvature elasticity, of nematic liquid crystals 410Ч11
Cylinders, drag forces on 266Ч7 283
Cylinders, flow past 147Ч8 252Ч62 279Ч83
Cylinders, lift forces on see Magnus effect
DarcyТs law 238
De Laval expansion nozzle 115 117
Depolarisation factors 139 40
Depressions 338Ч9
Die swell effect 402
Diffusion equation 26 242
Diffusivity, thermal 305
Diffusivity, viscous 304 (see also kinematic viscosity)
Dilatancy 407
Dimensional analysis 8Ч12
Director, in uniaxial liquids 390
Discharge rate, between parallel plates 208 214
Discharge rate, in pipe flow 30Ч31 221 351 3 374
Discharge rate, of a source or sink 124
Disclinations, in nematic liquid crystals 412Ч13
discs see plates; Rayleigh disc
Dispersion relations for quasi-particles in Helium 2 419
Dispersion relations for surface waves 171 174 176 177 294
Dissipation, of energy due to viscosity 8 21 204Ч6
Drag coefficients 136 264Ч8 274 283
Drag crisis 266Ч7 269Ч70
Drag forces 113Ч14 136 264Ч8 275Ч9
Drag, reduction of 268Ч70
Dynamical similarity 11 256
DТAlembertТs paradox 136 264
Eddies 254Ч61 263 279Ч81 348Ч9
Eddy conductivity (thermal) 379Ч81
Eddy viscosity 227 346Ч7 358Ч62
Effusion 93
Ekman layer 225Ч7
Electromagnetic analogues 127Ч9 136 139Ч40 141Ч2 144Ч6 147 158 275
Energy cascade, in homogeneous turbulencc 354Ч8
Enthalpy 87Ч9
Entrainment 76Ч7 368Ч9
Equation of state, of ideal gas 82
Euler strut 291
EulerТs equation 38 48 79 86
Excess pressure 49
Expansion fans 112Ч15
Explosions, effects of 105Ч7
Extensional viscosity 392
Fairings 268
Fans 61 64Ч5
Feigenbaum number 350
Flow alignment 398 400
Flow birefringence 394Ч8
Flow tube 13 46Ч7
Flowlines see lines of flow
Fluidity 2Ч3
Fohn 90
Form drag 264
Fountains 56
Froude number 186
Grashof number 306
Gravity waves 65Ч72 170Ч3 176Ч82
Guided waves 179Ч180
Gulf Stream 225
Hagen Ч Poiseuille law see PoiseuilleТs law
Hele Ч Shaw flow 218Ч220 297Ч302
Helicopters 61Ч3
Helium, properties of 415Ч22
Homogeneous turbulence 345Ч6
Homogeneous turbulence, energy spectrum of 354Ч8
Hydraulic jumps 71 2
Hydrostatics 49
Images, of vortex lines 156Ч7 159
Induced drag 267 275Ч8 279
Inertial sublayer, in turbulent shear flow 372
Inertial subrange, in spectrum of turbulence 356
Inlet length, in pipe flow 29Ч31 36
Instabilities, associated with convection 314 31
Instabilities, of arrays of vortex lines 331Ч2
| Instabilities, of boundary layers 340
Instabilities, of fluid-fluid interfaces 61 293Ч302
Instabilities, of nematic liquid crystals 411Ч13
Instabilities, of Stokes waves 33 341
Instabilities, of vortex sheets 331Ч6
Instability 32 289Ч93
Intensification by stretching, of vorticity 152Ч3 241 354
Intermittency, in turbulent flow 344 351 354
Inverse Magnus effect 281
Irrotational flow see potential flow
Jet stream 339
Jets 56Ч60 (see also submerged jets)
Joule Ч Kelvin effect 88Ч9
Journal bearings 217Ч18
Karman constant 372
Karman vortex streets see vortex streets
Kelvin wedge 190Ч4
Kelvin Ч Helmholtz instability 331Ч9 353
KelvinТs theorem 23 120Ч2
Kinematic viscosity 8 152 267 304
Knudsen flow 25 84 86 93
Kolmogorov scale length 356
Kolmogorov Ч 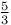 power law 356 power law 356
Korteweg-de Vries (KdV) equation 181
Kozeny Ч Carman relation 237
KundtТs tube 287
Laminar flow 206Ч7
LaplaceТs equation 23 120
LaplaceТs equation, solutions of 129Ч33 167
Law of the wall 372 375Ч6
Lift coefficient 274
Lift forces 114 273 4
Line vortices 240
Lines of flow 12Ч13 240
Lines of force 12Ч13 240
Lines of vorticity 240Ч3
Liquid crystals 386 409
Logarithmic law of the wall see law of the wall
Lubrication, hydrodynamic 214Ч18
Mach angle 108 111 112 113
Mach number 7Ч8 102 107
MachТs construction 109Ч11 192 4
Magnetohydrodynamics 415
Magnetostatic analogues see electromagnetic analogues
Magnus cffect 147Ч50 259 279Ч83
Marangoni convection 322
Marginal stability 290 292
Maxwell relaxation time 389Ч90
Mean free path, in gases 3 24Ч5 84Ч6 99 359 431Ч2
Mixing layers 347Ч8 369
Mixing length 347 361
Momentum equation see EulerТs equation
Momentum of gravity waves 173
Momentum of quasi-particles in Helium 2 419
Momentum of sound waves 99Ч101
Navier Ч Stokes equation 202 4
Nematic liquid crystals 390 399 409
Nematic liquid crystals, alignment of director in 399 409Ч12
Newtonian fluids 4 195Ч8
NewtonТs Law of Cooling 303
Non Ч NEWTONian fluids 384Ч7
Numerical methods 204 252 280
Nusselt number 306 308
Onsager relations 391
Open syphon effect in Helium 2 417Ч18
Open syphon effect in polymeric liquids 401
Open-channel flow 209Ч11
Oseen Ч Lamb model, for vortex line 224
Overstability 292Ч3
Parallel plates, flow between 207Ч9 213Ч14 369Ч74
PascalТs theorem 6 7 20
Pathlines 12
Pattern formation 302
Percolation 236Ч8
Period doubling 344 349Ч50
Permeability, of porous solid 238
Phonons 100 419
Pipe flow 29Ч31 34 221 345 351 4
Pitot tube 51
Planing, of boats etc 187Ч8
Plasma oscillations 413
Plasmas, properties of 413Ч15
Plasticity 3 384Ч5
Plates, drag forces on 113Ч14 246 267Ч8 378
Plates, flow past 27Ч28 111Ч15 143Ч4 243Ч51 269Ч71 375Ч8
Plates, lift forces on 114
Plug-hole vortex 44Ч6
Plumes 382
PoiseuilleТs law 31 221
Polar front 338Ч9
Polymer additives, effects on pipe flow of 405Ч7
Polymeric liquids 385
Polymeric liquids, non Ч Newtonian effects in 400Ч7
potential flow 21Ч3 119Ч77
Potentials 119Ч20
Potentials, complex 130Ч1
Potentials, multi-valued 144Ч5
Prandtl number 306
Pressure, mean 6 198 201Ч2
Rankine fairing 126 268
Rankine model, for vortex line 151
Rankine Ч Hugoniot relations 102Ч3
Rate of change, following fluid motion 39
Rate of deformation 199Ч200
Rayleigh disc 141 4
Rayleigh number 306 308
Rayleigh Ч B nard instability 314Ч19 nard instability 314Ч19
Rayleigh Ч Plateau instability 295Ч6
Rayleigh Ч Taylor instability 293Ч5
Reattachment, of boundary layers 256
Refraction, of ocean waves 66
Relaxation time, in liquids see Maxwell relaxation time
Reptation 400
Reynolds number 7Ч8
Reynolds Number in boundary layer flow 314 340
Reynolds Number in flow past cylinders 253
Reynolds Number in flow past plates or aerofoils 27Ч8 267
Reynolds Number in flow past spheres 228
Reynolds Number in pipe flow 7Ч8
Reynolds Number in suspensions undergoing shear 234 394
Reynolds Number in turbulent flows 357Ч358 363
Reynolds Number of vortex ring 263
Reynolds stress 359
Rhcology 386
Rheometers 386 405
Rheopexy 409
RiemannТs treatment, of sound propagation 425Ч8
Ripples 173Ч4 178
Rocket engines 93 115Ч18
Roll parameter 279
Rolls in convecting fluid 316Ч21 327Ч8 329Ч30
Rolls in nematic liquid crystals 411Ч13
Rotons, in Helium 2 419
Saffman Ч Taylor instability 297Ч302
Sailing boats 278Ч9
Scale models, use of 11Ч12 267
Scaling theories, of turbulent shear flow 347 362Ч78
Second sound, in Helium 2 418
Second viscosity see bulk viscosity
Secondary circulation 213 283Ч8
Self-preserving flows see self-similarity
Self-similarity of laminar boundary layer flow 244
Self-similarity of turbulent shear flows 347 363Ч4
Separation, of boundary layers 253Ч6 261Ч2 263 271 280
Shadowgraphs 337 347
Shear modulus of plasma threaded by magnetic field 415
Shear modulus of viscoelastic substance 387Ч9
Shear shedding, of eddies 259Ч61 279Ч81
Shear thickening 405 408
Shear thinning 405 408Ч9
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 n waves
n waves 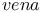
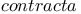
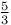 power law
power law