|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ticciati R. — Quantum field theory for mathematicians |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Spectator processes 520
Spectral function 314
Spectral function, formula for field renormalization factor 315
Spectral function, formula for imaginary self energy 317
Spectral function, formula for renormalized propagator 316
Sphalerons 474
Spherical pendulum 37—40
Spin-statistics theorem 465
Spin-sum, spin-average 221
Spinor see "Dirac polarization spinor" "Weyl
Spinor field see "Dirac field" "Weyl
Spinor representations 167—170
Splitting of representations 142
Splitting of representations, SU(3) 441 446 447 450 451
Spontaneous symmetry breaking 53 69 398
Spontaneous symmetry breaking,  model 501 model 501
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, chiral SU(2) 502
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, classical 398—401
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, dynamical 670
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, global example 399
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, local example 400
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, quantization 404—406
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, Weinberg — Salam model 457
Standard model 69 454
Standard Model, four-lepton operators 508
Standard Model, lepto-quark operators 508—522
State in and out 277—281
State space, discrete 5
State space, Fock space 14
State space, one-particle 2—5
State, ideal 3
State, localized 278
State, one-particle 277
State, physical 3
State, two-particle 280
Stationary phase in functional integral quantization 336
Strange hadron decays 522
Strange representation 84
Stress-energy tensor 64
Strictly renormalizable theories 605
String theory 664
Strong CP problem 477
Strong force 465
Strong interactions 438
Strong interactions, PT symmetry 523 see
Structure constants 146 388 389 390
SU(2) 147—153
SU(2) global anomaly 475
su(2), tensor products 158
SU(3) global anomaly 475
SU(3) representation theory 439—453
SU(N) 57
Subdiagram 600
Subdiagram, collapsing 603
Subrepresentation 143
Super-renormalizable theories 605
Superdeterminant 619
Superficial degree of divergence 597—599
Superselection rule 69 71 203
Supersymmetry 663
Survival amplitude 319
Symmetric Lorentz tensors 163
Symmetric operator 344
Symmetric point 294 299
Symmetric representations of SU(3) 450
Symmetrical ordering 335
Symmetry 37—67
Symmetry breaking see "Spontaneous symmetry breaking"
Symmetry condition 38
Symmetry condition, infinitesimal 39 42
Symmetry, anomalous 412
Symmetry, discrete 70—78
Symmetry, electroweak 69
Symmetry, external 47
Symmetry, factor 88—93 106 273
Symmetry, generator 59 390
Symmetry, internal 47
Symmetry, linear 54
Symmetry, rotation 37—40
Symmetry, SO(2) 48—53
Symmetry, translations 64
Table of Dirac fields and particles 218
Table of discrete symmetries and Fermi bilinears 240
Table of helicities 182
Table of pseudoscalar mesons 444
Table of Weyl fields and particles 189
Tadpole diagram 117 220
Tadpole renormalization condition 291
Taylor expansion 601
Tensor product 154—158
Tensor product, so(1, 3) representations 161
Tensor product, SU(3) representations 446
Tensor representations of SU(3) 447—451
Time ordering 21 83
Time ordering and calculus 283
Time ordering, exponential 83
Time ordering, Fermi fields 186
Time reversal 74—77
Time reversal, Dirac fields 236—239
topology 428—430
Trace trick for squaring amplitudes 197 221 228
Trajectory 37
Transition probability 122
Translation 5 64
Translation, unitary representation 5
Triangle diagram 559—561
| Turning on and off function 80 119 269 288
Two-component spinor see "Weyl polarization spinor" "Weyl
Two-particle states 280
U(1) symmetry 180 216 265
U(n) 55 56 57
Undefined constants 334
Unification in physics 662—665
Unified field theories 664
Unitarity gauge 403 457
Unitarity of the S matrix 133 397
Unitary group see "U(n)"
Unitary representation 61
Unitary representation of Lie algebras 143
Unitary representation of Lorentz group 7
Unitary representation of parity 72
Unitary representation of permutation group 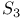 484 484
Unitary representation of Poincare group 9
Unitary representation of SO(2) 50
Unitary representation of SU(3) 439—453
Unitary representation of translations 5
Unitary representation, charge conjugation 70
Unitary representation, complex conjugation 439
Unitary representation, condition for 137
Unitary representation, even and odd 450
Unitary representation, many-valued 50
UNITS 1
Unstable particle 134 317—326
Unstable particle and causality 320
Unstable particle, modeling 321—322
Vacuum state 14 16 30—34
Vacuum to vacuum amplitude 270
Vacuum, bubble diagrams 101
Vacuum, evolution of 98
Vacuum, free 275
Vacuum, functional 33
Vacuum, insertion 517
Vacuum, physical 274
Vacuum, polarization 118
Vacuum, renormalization condition 291
Variation, BRS 619
Variation, complex field 52
Variation, Dirac field 350
Variation, fixed-endpoint 337
Variation, gauge 266 607
Variation, Weyl field 204
Vector bundle 262
Vector field 246
Vector field, Hamiltonian 250
Vector field, massive 248
Vector representation 439
Vector representation, so(1, 3) 163
Virtual particle 105
W gauge fields 457
W mass 459
Ward identity and abelian anomaly 561
Ward — Takahashi identities 612—617
Ward — Takahashi identity 607—610
Wave packet 232 249 278 326
Wave-packet creation and annihilation operators 279—280 303 310
Weight diagram 145
Weight diagram, SU(3) 446
Weight diagram, tensor products 155—156
Weights 145
Weights, addition of 155
Weinberg angle 458
Weinberg — Salam model 454 455—457
Weinberg — Salam model, fermion currents 461
Weinberg — Salam model, gauge fields 458
Weinberg — Salam model, Lagrangian 456
Weinberg — Salam model, lepton-boson couplings 460
Weinberg — Salam model, quantum numbers 69
Weinberg — Salam model, tree-level operators 463
Weinberg's convergence theorem 600
Weyl field 177—198
Weyl field, conjugate 200
Weyl field, invariant terms 170
Weyl field, massive 204—206
Weyl field, plane waves 174
Weyl field, table of particles 189
Weyl ordering 335
Weyl polarization spinor 167—170 174
Weyl polarization spinor, completeness relations 176
Weyl polarization spinor, index conventions 198—199
Weyl polarization spinor, normalization relations 176
Weyl polarization spinor, phase ambiguity 175
Weyl representation 208
Wick diagram 87—88 190 348
Wick diagram, connected 93
Wick diagram, disconnected 93
Wick expansion 87
Wick operator 88—90
Wick rotation 297 300 338—339 365 417 473 535
Wick vertex 88 190 254 356 368
Wick's Ordering Theorem 86
Wightman's triviality theorem 19
Wigner — Eckart theorem 500
Wigner's operator theorem 74
Wilson 665
Winding number 429
Yang — Mills theory 389 617
Yang — Mills theory with matter fields 390—393
Yang — Mills theory, RGE 655
Young diagrams 451—453
Yukawa potential 99 115
Z gauge field 458
Z mass 459
Zimmermann 600
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 model
model