Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Jones N.D. — Computability and complexity from a programming perspective
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Computability and complexity from a programming perspectiveАвтор: Jones N.D. Аннотация: "Neil Jones is one of the precious few computer scientists with great expertise and leadership roles in both formal methods and complexity. This makes his book especially valuable." — Yuri Gurevich, Professor of Computer Science, University of Michigan
Язык: Рубрика: Computer science /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1997Количество страниц: 457Добавлена в каталог: 01.12.2013Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
384 394 393 434 356 350 see 349 349 222 434 63 60 61 29 2CM 127 135 2DFDA 359 Acceptable enumeration 227 Acceptance see "Decision" Acceptance by a non-deterministic program 331 Acceptance by finite automata 437 Accepting states 437 Ackermann's function 97 104 Algorithm 9 Alphabet 431 Alphabet, tape 115 Annotated program 106 110 Approximation xv Asymptotic 299 300 atom? 33 Atoms (definition) 28 Automata, finite 436 BACC 407 Binding-time engineering 96 Bit strings, related to binary trees 250 Bitwise less-than 172 Blum's speedup theorem 307 Boolean algebra, quantified 409 Boolean expression 419 Boolean operators 419 Boolean programs, acceptance see "Bacc" Boolean programs, defined 383 Boolean programs, nontriviality 398 Boolean variables 419 Busy beaver 16 C 434 Cartesian product 422 case command 39 CFALL 161 434 CFAMB 161 434 CFG see "Grammar context Church — Hiring thesis 4 8 127 Church — Rosser Theorem 142 Church — Turing — Kleene thesis 205 Circuit complexity xv 9 Circuit, monotone 383 388 CLIQUE 367 369 370 cm 111 116 see CM-computability 127 208 CM-computable 134 208 CMro 317 319 CNF 367 370 420 Communicating systems xv Compilation 50 59 Compilation for proving equivalence of languages 127 Compilation versus interpretation 91 Compilation with change of data 52 129 Compiler 50 53 231 Compiler, bootstrapping 93 Compiler, diagrams 51 56 Compiler, generation 97 Compiling function 50 Compiling function, w.r.t. coding 53 Complete logical Systran 196 198 Complete problems 365 372 374 Complete problems for NLlNTIME 378 Complete problems for NLOGSPACE 376 380 Complete problems for NPTIME 397 Complete problems for PSPACE 407 Complete problems for PTIME 383 Complete problems for RE 375 Completeness 365 Complexity classes see "Completeness" "Complete Complexity classes, characterizaton without resource bounds 349 Complexity classes, definition of 271 Complexity classes, LINTIME 272 276 Complexity classes, non-deterministic 333 Complexity classes, PTIME 272 275 Complexity classes, relations among 322 324 333 345 346 Complexity classes, robustness of 276 Complexity classes, space classes, definition of 319 333 Complexity classes, space classes, LOGSPACE 319 Complexity classes, space classes, PSPACE 319 322 Complexity classes, space classes, robustness of 322 Complexity classes, time, classes PTIME 244 Complexity classes, time, definition of 333 Complexity classes, time, robustness of 273 276 composition 206 Composition of (primitive) recursive functions 206 Composition of compiler and interpreter diagrams 56 Composition of functions, symbolic 228 Composition of general functions 426 Composition of space-bounded programs 326 Computable 75 Computable function 205 see "Decidable" "Effectively "Equivalence "Recursive "WHILE Computable in linear time and size 378 Computable in logarithmic space 325 Computation model, CM 116 Computation model, machine models see "CM" "RAM" "SRAM" Computation model, RAH 118 Computation model, read-only see also "CMro" "TMro" Computation model, SRAM 119 Computation model, TM 115 Computation models, comparison of times 251 273 Computation models, default for complexity classes 335 Computation models, effect on complexity theory 20 241 Computation models, equivalence v.r.t. computability 127 Computation models, fair time measures 254 Computation models, introduced 111 Computation models, read-only 247 316 Computation models, space measures 316 Computational completeness of a spedalizer 102 Computational completeness, hiring completeness 227 Computational completeness, optimality of a spedalizer 103 Computationally tractable 20 Concrete syntax 48 53 143 336 conditionals 32 Configuration 337 Configuration string 155 Conjunction 32 192 419 Conjunctive normal form see "CNF" cons 35 Cons-ffee programs 349 355 Cons? 33 Conservative extension 93 Consistent logical system 196 198 Constant time factor 290 Constant time factors 243 285 290 Constructible 293 Constructible, space 328 Context-free grammar see "Grammar" Context-sensitive grammar see "Grammar" Convergent 10 Cook's construction 288 359 Cook's thesis 20 242 Counter machine see "CM" Currying 428 Cyde 431 Dag 261 431 DAG semantics 264 Data sharing 261 Data-storage graph 261 Davis — Putnam — Robinson theorem 176 Decision problems 243 Deddable 76 Deddable in linear time 272 Deddable in logarithmic space 319 Deddable in polynomial space 319 Deddable in polynomial time 272 Deddable in space f 319 Deddable in time f 272 Derivation relation 153 Deterministic finite automaton 437 DFA 437 diag 290 328 Diagonal argument see "Diagonalization" Diagonalization 14 290 328 Diophantine equations 169 Directed graph 431 Disjoint 422 Disjunction 32 192 419 Distributed computing 258 Divergent 10 Divide-and-conquer search 341 DL 198 Dovetailing 81 87 299 DSG 261 Edges 430 Effective procedure 3 Effectively computable 11 Effectively decidable 13 Effectively enumerable 13 Effectively solvable 4 Encoding in compilaxious with change of data 129 Encoding of bit strings in trees 250 Encoding of problem input 368 Encoding of trees in bit strings 251 Encoding, booleans as trees 32 Encoding, integers as trees 34 Encoding, many atoms using one 63 73 Encoding, numbers as bit strings 131 Encoding, programs in numbers (Goedel) 205 Encoding, sequences in numbers (Matiyasevich) 171 Entscheidungsproblem 23 Enumerable 76 Enumeration 14 Environment 189 Equation solving 232 Equation, Diophantine 169 Equation, exponential Diophantine 169 Equivalence of 208 Equivalence of languages with respect to complexity 252 Equivalence of languages with respect to computability 48 Evaluation 36 execution 36 Existential quantifier 193 Explicit transformation 206 Expression, evaluation 189 Extensional 226 240 f 137 275 291 F+ro 349 FALSE 32 419 Finite automaton 256 436 First component 422 fixpoint 215 221 230 Fixpoint iteration 218 Formula 419 Function 422 function call 137 Function, Ackermarnn's 97 104 Function, addition 426 Function, argument 423 Function, bijective 428 Function, codomain of 425 Function, composition 426 Function, computable in logarithmic space 325 Function, computing a 10 Function, converging 424 Function, defined 424 Function, defined inductively 439 Function, definedness 422 Function, diverging 424 Function, division 427 Function, domain of 425 Function, double 423 Function, exponential polynomial 169 Function, injective 428 Function, inverse 444 Function, logarithmic 429 Function, maximum 429 Function, minimum 429 Function, monotonic 429 Function, monus 423 Function, multiplication 426 Function, one-to-one 428 Function, onto 428 Function, pairing 442 Function, partial 424 Function, polynomial 169 Function, predecessor 423 Function, range of 425 Function, recursive 205 Function, recursively defined 439 Function, result 423 Function, semantic 47 Function, strictly monotonic 429 Function, subtraction 426 Function, surjective 428 Function, total 423 Function, undefined 424 Function, uniqueness 422 Function, updating 426 Futamura projections 98 Game 394 Game complexity 415 Gap 367 Gap theorem 311 Garbage collection 270 Goedel numbers 205 Goedel's incompleteness theorem 198 goto 111 Goto-free 383 GOTOro 349 Grammar 432 Grammar, ambiguous 161 434 Grammar, context-free 160 433 Grammar, context-free, decision problems for 160 393 434 Grammar, context-free, definition 433 Grammar, context-sensitive 433 Grammar, context-sensitive, decision problems for 415 Grammar, context-sensitive, definition 433 grammar, regular 433 435 Grammar, regular, decision problems for 412 434 Grammar, regular, definition 433 Grammar, set generated by 433 Graph 430 Graph, accessibility 338 Graph, acyclic 431 Graph, algorithm 338 339 341 342 Graph, building 343 Graph, cyclic 431 Graph, directed 430 Graph, inaccessibility 339 Graph, searching 338 Graph, state transition 337 Halting problem 77 Hardware viewpoint 9 Hierarchy 285 291 365 Higher-order function 427 Hilbert's choice function 212 Hilbert's program 23 Hilbert's tenth problem 167
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



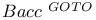
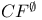
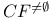
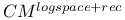
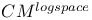
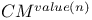
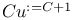
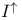
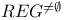
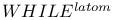
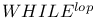
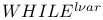
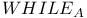
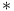
 -recursiveness
-recursiveness