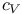Ideal gas in classical limit, classical partition function 239Ч241 245
Ideal gas in classical limit, density of states 64Ч66
Ideal gas in classical limit, entropy 160
Ideal gas in classical limit, entropy, quantum expression for 362
Ideal gas in classical limit, equation of state 125 241
Ideal gas in classical limit, internal energy 126 153Ч156
Ideal gas in classical limit, mixture of several species, chemical potential 322
Ideal gas in classical limit, mixture of several species, equation of state 321
Ideal gas in classical limit, mixture of several species, partition function 321
Ideal gas in classical limit, quantum calculation of partition function 360Ч361
Ideal gas in classical limit, specific heat relations 156Ч157
Ideal gas in classical limit, validity of classical approximation 246Ч348
Ideal gas in quantum limit 331Ч362 see
Impact parameter 463
Information theory 231
Intensive parameter 149
Internal energy 122
Internal energy of ideal gas 126 153Ч155
Internal energy of van der Waals gas 174
Internal energy, general volume dependence of 173
Internal energy, measurement of 129Ч131
Internal energy, relation to partition function 213
Inverse collision 522
Inverse transition 546
Inversion curve 181
Irreversibility, and microscopic reversibility 599Ч600
Irreversible process 91Ч93
Ising model 429
Isotherm 307
Isothermal process 158
Isotope separation by effusion 276
Joule 3 155Ч156
Joule Ч Thomson coefficient 181Ч182
Joule Ч Thomson process 178Ч184
Joule, free expansion experiment 155
Kammerlingh Onnes 455
Kelvin 8 181
Kelvin temperature scale 136
Kinetic theory 3 262Ч281 461Ч545
Kirchhoff's law 385
Knudsen gas 477
Kronecker delta symbol 616
Kronecker delta symbol, integral representation of 616 618
Lagrange multipliers 621Ч622
Lambert's law 387
Langevin equation 564
Latent heat 304
Lattice as totality of all nonspin degrees of freedom 554
Lattice, vibrations in solid 407Ч414
Le Chatelier's principle 298
Le Chatelier's principle and chemical equilibrium 325
Le Chatelier's principle and compressibility 300
Le Chatelier's principle and heat capacity 298Ч299
Lennard-Jones potential 419
Liouville's theorem 628
Macroscopic system 2
Macrostate 66
Magnetic cooling 445Ч451
Magnetic resonance 553Ч556
magnetic susceptibility 440
Magnetic work 440Ч444
Markoff process 677
Mass action, law of 322Ч324
Master equation 549
Master equation for system in contact with heat reservoir 553
Maxwell 3
Maxwell relations 164Ч166
Maxwell velocity distribution 210 264 267
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics 343Ч345
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics and absence of symmetry requirements 332
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics and counting of states 337
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics as limiting case of BE and FD statistics 351Ч353
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics, distribution function for 345
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics, fluctuations in particle number 345
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics, partition function for 344
MB see "Maxwell Ч Boltzmann statistics"
Mean free path 465
Mean free path, related to scattering cross section 471
Mean values 11Ч13
Mean values for continuous variables 28Ч29
Mean values for random walk 14Ч16 33Ч34
Mean values of a product 26
Mean values of a sum 12 26
Mean values of Gaussian distribution 24
Mean velocities of molecule in a gas 265Ч269
Mechanical interaction 68Ч72
Melting 305n
microcanonical ensemble 202
Microscopic reversibility 384 598
Microscopic reversibility, relation to macroscopic irreversibility 599Ч600
Microscopic system 2
Microstate 51
Molecular beam 274
Molecular beam for measuring velocity contribution 274Ч276
Molecular chaos 523
Molecular distribution in gravitational field 210Ч211
Molecular distribution of velocities 209Ч210 264
Molecular field 430
Molecular partition function for electronic motion 368Ч369
Molecular partition function for rotation 369Ч371
Molecular partition function for translation 368
Molecular partition function for vibration 371Ч372
Molecule in a gas, distribution of speed 267Ч268
Molecule in a gas, distribution of velocity 209Ч210 262Ч264
Molecule in a gas, distribution of velocity component 265
Molecule in a gas, mean kinetic energy of 250
Molecule in a gas, mean velocities of 265Ч269
Moments of a probability 13
Noise in electric circuit 587Ч588
Noise, relation to Brownian motion 560
Noise, thermal, associated with electrical resistor 588Ч589 see
Noise, white noise 589
Normal coordinates 408
Normalization condition for probabilities 12
Normalization condition for probabilities for continuous cass 28 29
Nyquist's Theorem 588Ч594
Nyquist's theorem as analogue of black-body radiation 592Ч593
Nyquist's theorem as special case of fluctuation-dissipation theorem 588Ч589
Nyquist's theorem for arbitrary impedance 591Ч592
Nyquist's theorem, derived from equilibrium considerations 589Ч591
Onsager symmetry relations 598Ч599
Overbauser effect 556Ч560
Paramagnetism in classical limit 284
Paramagnetism of atoms with spin 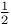 206Ч208 206Ч208
Paramagnetism of conduction electrons in a metal 401
Paramagnetism of interacting atoms 432Ч434
Paramagnetism, general case 257Ч262
Partial derivatives relations between 619Ч620
Partial pressure 321
Particle, moving freely in a box, density of states 358
Particle, moving freely in a box, quantum states 49 354Ч360
Partition function 213
Partition function for noninteraction systems 238Ч239
Partition function of classical ideal gas 240Ч245
Partition function, properties of 237Ч239
Partition function, relation to Helmholtz free energy 216
Path integral method 503Ч504
Pauli exclusion principle 333
Perrin 567
Persistence of velocity 489n 516
Persistence of velocity, effect on electrical conductivity 583Ч534
Phase-equilibrium line 303
Phase-equilibrium line, slope of 304
Phass space 50Ч51 59
Phass space for harmonic oscillator 55Ч56
Phass transformation and equation of state 306Ч312
Phass transformation of superconducting metal 458
Phass transformation, equilibrium conditions for 301Ч304 315Ч317
Phonons 405 409
Phonons, contribution to thermal conductivity of solids 483
| Phonons, temperature dependence of number of 416
Photon statistics 345Ч346
Photon statistics as special case of BE statistics 338
Photon statistics, distribution function for 339Ч340 346
Photon statistics, distribution function for, as special case of BE distribution 342 349
Photon statistics, fluctuation in particle number 346
Photon statistics, partition function for 345
photons 373Ч374 see
Planck distribution 340 346
Planck radiation law 388
Poise 473
Poiseuille flow through tubes 491
Poisson distribution 41Ч42
Polarization of spins by dynamic methods 556Ч560
Polarization of spins by large constant field 238 261 657
Postulate of equal a priori probabilities 54Ч56
Pressure of gas mixture 282
Pressure tensor 472n
Pressure, calculated by statistical mechanics 125 241
Pressure, exerted by a gas 398Ч399
Pressure, exerted by degenerate Fermi Ч Dirac gas 401
Pressure, kinetic evaluation of 278Ч281
Pressure, related to momentum transfer 278Ч281
probability 5
Probability of several variables 25Ч26
Probability of statistically independent variables 26
Probability, density 22 27Ч32
Product molecule 318
Quantum states of free particle 49 364Ч360
Quantum states of harmonic oscillator 49
Quasi-particles 404Ч405 409
Quasi-static process 74Ч76
Radiation emitted by a body 381Ч388
Radiation emitted by a body and black bodies 386
Radiation emitted by a body, Planck radiation law for 388
Radiation in equilibrium 378Ч381
Radiation in equilibrium, energy density of 375Ч376
Radiation in equilibrium, general properties of 378Ч381
Radiation in equilibrium, photon distribution for 374
Radiation in equilibrium, pressure of 377Ч378
Radioactive decay 42
Random walk 5Ч40
Random walk and diffusion 486Ч488
Random walk with arbitrary step lengths 32Ч40
Random walk with arbitrary step lengths, mean values 33Ч34
Random walk with arbitrary step lengths, probability distribution 35Ч36
Random walk with arbitrary step lengths, probability distribution for large N 37Ч40
Random walk with equal step lengths 7Ч11
Random walk with equal step lengths for large N 17Ч21
Reactant molecule 318
Reduced mass 517
Refrigerators 190Ч161
Refrigerators, perfect 190
Relaxation rates 93Ч94
Relaxation time 59
Relaxation time as time between molecular collisions 465
Relaxation time for spin system 556
Relaxation time in Boltsmann equation 509
Reverse collision 521Ч522
Reverse transition 384
Reversible process 91Ч93
Rigid rotator 369Ч371
Rotation of molecule 369Ч371
Saturation in magnetic resonance 556
Saturation of magnetization for large H/T 208
Scattering cross section 467Ч468
Scattering cross section, differential 468 520
Scattering cross section, differential, effect of time reversal and space inversion 521Ч522
Scattering cross section, total 468
Scattering cross section, total, for hard spheres 469
Second law of thermodynamics 122Ч123
Second law of thermodynamics and canonical distribution 215
Second law of thermodynamics, Clausius statement of 191
Second law of thermodynamics, Kelvin statement of 186
Self-diffusion see "Diffusion"
Semipermeable membrane 148
Smoluchowski equation 580
Sound, velocity of 195
Space inversion effect on scattering cross section 522
Specific heat 139
Specific heat of conduction electrons in metals 391Ч393
Specific heat of conduction electrons in metals, exact calculation of 396Ч397
Specific heat of diatomic molecules 399
Specific heat of monatomic ideal gas 157Ч158 241Ч242 251
Specific heat of solids 253Ч256
Specific heat of solids in classical limit 253Ч254 411
Specific heat of solids, Debye theory 416
Specific heat of solids, Einstein approximation 254Ч255
Specific heat of solids, general expression 411
Specific heat, behavior as 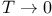 170 170
Specific heat, general relation between 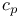 and and 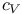 166Ч163 166Ч163
Specific heat, positive sign of 298
Specific heat, volume dependence of 171
Spectral density 585
Stationary ensemble 584
Statistical independence 25Ч26
Statistical mechanics 3
Steady state 462
Stefan Ч Boltzmann constant 388
Stefan Ч Boltzmann law for radiation energy density 376 388
Stefan Ч Boltzmann law for radiation energy density, thermodynamic derivation of 399
Stirling's formula 613
Stirling's formula to lowest approximation 611
Stirling's formula, including correction terms 614
Stokes's law 565 601
Stress in fluid 472
Sublimation 305n
Substantial derivative 531
Summation convention 526
Superconductivity 438 455Ч458
Superconductivity, critical field 455
Superconductivity, critical temperature 455
Superconductivity, entropy and latent heat 458Ч469
Superconductivity, magnetic moment 456Ч457
Superconductivity, slope of critical temperature curve 458
Superfluid liquid helium 438
Surface tension 196Ч197
Survival probability 463
Susceptihility, magnetic 208
Susceptihility, magnetic, in general case 261
Temperature 102Ч106
Temperature as arbitrary thermometric parameter 104
Temperature, absolute 105
Temperature, absolute, measurement at very low temperatures 452Ч455
Temperature, absolute, measurement of 133Ч137
Temperature, absolute, negative 105
Temperature, absolute, properties of 105Ч106
Temperature, absolute, spin 105 556
Temperature, absolute, statistical definition of 99
thermal conductivity 478Ч479
Thermal conductivity of conduction electrons in metals 51
Thermal conductivity of dilute gas 479Ч481
Thermal conductivity of dilute gas, calculation in terms of r 514Ч515
Thermal conductivity of dilute gas, related to viscosity 481
Thermal conductivity of dilute gas, rigorous calculation 546
Thermal conductivity of solids 482Ч483
Thermal conductivity, coefficient of 479
Thermal insulation 68
Thermal interaction 66Ч68
Thermionic emission of electrons 402
Thermodynamic functions 166
Thermodynamic laws 122Ч123
Thermodynamics 3
Thermometers 102Ч105
Throttling process 178Ч184
Time average 583
Time reversal 383Ч384
Triple point 305
Triple point of water 135Ч136
Trouton's rule 330
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



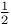
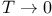
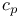 and
and