|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Pearl J. — Heuristics |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Heuristics, relaxation-based 11 113—116 118—124
Heuristics, typical uses 6—13 52—54
Hill-climbing 35 65 71 121
Hillier, F.S. 31
Hofstadter, D.R. 322 325
Horowitz, E. 26 69 133
Huffman code 26 32 133
Hummel, R. 69
Huyn, N. 171 175 176 177 180 181
Hybrid strategies 65—69 126 151 281
Hypergraphs 23
Hyperpaths 25
Ibaraki, T. 21 31 67
Immortality in branching processes 155 165
Incremental search 4 10
Influence functions, in games 235
Informed ordering, in games 287 294 299 310—317 324—325
Informed search 34 46—56
Informedness, of heuristic functions 79 81 111 169 177 200 311 334 337
Irrevocable strategies 35 68
Jelinek, F. 71
Johnson, D.S. 10
Kadane, J.R. 130 134 325
Kahneman, D. 124 125
Kalah 249—250
Kanal, L. 31 286
Karp, R.M. 11 31 131 150 162 163
Kibler, D. 131
Kim, J.H. 111
Kister, J. 286
Kling, R.E. 118
Knuth, D.E. 234 269 286 287 294 298 348
Korf, R.E. 131
Kowalski, R. 31
Kuczma, M. 258 328
Kumar, V. 31 286
Labeling procedures 45 51 58—60 224
Labeling rules 25 58
Lagrange relaxation 131
Largely dominates 85 107 112
Law of Large Numbers 125
Law, A.M. 61 102
Lawler, E.L. 19 31 70 131
Lea, W. 163
leaf nodes 33
Leaf nodes of a search tree 49
Leaf nodes, deep and shallow 319
Leal, A. 29
Lenat, D.B. 118 131
Lieberman, G.J. 31
LIFO search strategies 36 39
Lin, S. 31
Linial, N. 31
Links (arcs), in graphs 22 33
Locally finite graphs 33 73 77
Logical reasoning 27 31
Look-ahead, bounded 162 227 229 286 332 347 351 357
Lowerre, B.T. 163
Loyd, S. 31
Mackworth, A.K. 31 69
Mahanti, A. 111 194
Manhattan distance 8 71 79 114 120
Marsland, T.A. 310
Martelli, A. 70 111 112 194
Massey, J. 31
Max-cost 34 58 62 101 281
Maximum-likelihood decisions 71
McCarthy, J. 273 286
Means-end analysis 29 122
Mercer, R.L. 71
Merge problem 32
Merit labeling, of solution graphs 58—60
Mero, L. 111
Metaphorical models 117—118
Michie, D. 31 70 120
Michon, G. 215 321 324 325 326 354
MINIMAX algorithms, backtracking version 229
MINIMAX algorithms, depth-first version 230
Minimax convergence theorem 256—257 272—273 286
Minimax convergence theorem for nonuniform trees 322
Minimax convergence theorem, applications 273—277
Minimax rule 60 227—228 286 332 358
Minimax rule, alternatives to 358—360
Minimax rule, error propagation for 333—347
Minimum spanning tree 11 33 36 79 115 124 176 210
Minker, J. 31
Monotone see Consistent heuristics
Montanari, U. 69 70
Moore, E.F. 69 275 286
Moore, R.W. 234 269 286 287 294 298 348
More efficient than 199—202
More informed than 79 81 111 177 200
Moses, J. 27
Most promising solution-base 60 51—53 60
Munyer, J. 163 170
Nau, D.S. 31 32 333 348 349 360 361
Near-optimization 15 88—90 150 162
NEG-MAX notation 228 234
Nemhauser, G.L. 31
Newborn, M. 285 348
Newell, A. 19 29 70 117 122 163 286
Nilsson, N.J. 29 31 49 61 63 68 70 77—84 110 111 123 286
Node expansion 34 36
Node expansion, condition for 79—81 84 107—110 141 146 148 173 194—199
Node generation 34 40
Node generation, condition for 238 295
Nodes, in graphs 22 33
Nodes, in graphs, critical 296 302
Nodes, in graphs, dummy 74
Nodes, in graphs, frontier 50 167
Nodes, in graphs, goal 6 74 191
Nodes, in graphs, mortal 155 160 164—165
Nodes, in graphs, off-track 76 191
Noe, T. 249
Normalized errors 184
NP-hard problems 10 15 162
Nudel, B. 69
Number-scrabble 117
Off-course subtrees 171—172
Off-track nodes 76 191
OPEN list 34 37 40
Open nodes 34
Operations research 19 31 55 70 131
Operators 16 20 35 74 see
Operators in STRIPS 119 122 133
Optimal solution graph 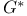 60 60
Optimality of solutions 19 43
Optimality of solutions near optimality 15 88—90 128
Optimality of solutions, approximate optimality 15 90—99 129 150 162 164
Optimality, of search algorithms 75 111 134 260
Optimality, of search algorithms, asymptotic 260 264
Optimality, of search algorithms, of 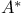 85 107 111—112 206—207 85 107 111—112 206—207
Optimality, of search algorithms, of 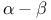 3 294 298 3 294 298
Optimality, of search algorithms, of SOLVE 264—266
Optimization tasks 14 41 54 70 128—134 192
OR links 22 26 27 222
OR nodes 25
Order of typical errors 184 189
Order-preserving heuristics 62 78 100—102
Ordering of successors, dynamic 286
Ordering of successors, in games 287 294 299 310—317 324—325
Overconstrained models 116—117
Palay, A. 359
Pang, C. 69
Parent discarding 55—62
Parent nodes, in graphs 33
Path-seeking problems 10 19 21 25—27 32 140—163
Pathology in game searching 332—361
Paths, in graphs 34 74
Paths, in graphs, C-bounded 80 81 84 111 112
| Paths, in graphs, cheapest 74 150—163
Paths, in graphs, cost of 34 74 151
Paths, in graphs, infinite 77 104 155 165
Paths, in graphs, shortest 62 69 140—150
Paths, in graphs, solution 75 103 104
Pearl, J. 29 85 107 110 111 118 124 131 150 163 171 175 176 177 180 181 184 189 246 258 277 286 294 297 298 325 327 333 359
Perfect discrimination function, 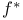 75—76 75—76
Peterson, W.W. 156
Pohl, I. 31 70 88 105 106 111 115 170 171 183 202 213
Pointer-paths 34 49 74 101 104
Pointers 34 74
Pointers, redirecting 48 49
Policy, of search see Search procedure
Precision and accuracy 199—201
Precision-complexity exchange 184 189—190 198
Precondition list, in STRIPS 119—121 123—124
Principle of optimality 76 102
Probabilistic algorithms 127
Probabilistic models for performance analysis of 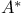 and backtracking 146 150 171—172 and backtracking 146 150 171—172
Probabilistic models for performance analysis of game searching 251—259 318—325 351
Probabilistic models for performance analysis, rationale for 139—140 170—171 309—310
Probability-based heuristics 124—131
Probability-based heuristics, examples 13 129 162—163 164
Problem—reduction representation 21 23 26 29 222
Product-propagation rules 358—360
Production rules 16 20 25 40
Program synthesis 26 137
Pruning 17 41 64 79 126 229
Pruning by dominance 21
Pruning, power 17 147 149 163 169
Puzzles 4 31 32
Quantiles 256 274 277 286
Rabin, M. 127
Range, as a cost measure 90 99 101
Raphael, B. 63 70 110 111
Recovery of pursuit 65
Recursive weight functions 57 100
Relaxed models 11 115 118—124
Reopening nodes 49 72 76 82 111 194
Representations 14
Representations, problem reduction 21 23 26 121—124
Representations, selection of 26 31
Representations, state space 20 24 26
Reproduction process 173 183
Risk of leaving nodes unexplored 93—94
Risk-admissibility 94 112
Road map problem 9 114 146—150
Roizen, I. 296 300 325 326
Rollback function 58
root node 33 225 259
Rosenfeld, A. 60
Rosenschein, S. 131
Ross, R. 70
Rubin, S. 163
rule of thumb 3
Sacerdoti, E.D. 29 131
Sahni, S. 26 69 133
Saleh, J. 29
Sampling 126
Samuel, A.L. 226 286
Satisficing 14 54 69 86 128 171 192 206
Scope of evaluation 65
Scout algorithm 246—250 286—287
SCOUT algorithm for searching flow trees 282
SCOUT algorithm, branching factor 291—292 317 326
SCOUT algorithm, definition 247
SCOUT algorithm, flowchart 248
SCOUT algorithm, motivation for 246 247
SCOUT algorithm, performance analysis 289—293
SCOUT algorithm, relation to  249—250 285 307—310 326 249—250 285 307—310 326
Search graph 49
Search procedures 33 34
Search procedures, blind 34 36—46
Search procedures, exhaustive 7 229
Search procedures, hierarchy of 63
Search procedures, hybrid 65—69 126 151 192
Search procedures, informed 34 46—56
Search procedures, irrevocable 35 68 131 151
Search procedures, performance analysis 137—140
Search procedures, systematic 4 16 35
Search procedures, tentative 36
Search spaces 14
Search tree 48 74—75
Seed nodes 349 361
Semi-decomposable problems 122
Semi-optimization tasks 15 41 86—99 128—134
Set-splitting argument 55 62 78
Set-splitting problem 26
Shannon, C.E. 273 275 286 299
Shapiro, J.F. 131
Shaw, J.C. 29 70 286
Simon, H.A. 14 19 29 31 70 117 130 134 286
Sint, L. 70
Slagle, J.R. 31 70 269 286 294
Small-is-quick principle 15 52 53 62 86 206
Solution bases 49—52 240
Solution bases, most promising 51 53
Solution bases, scoring of 50—54 240
Solution graph 23—25
Solution graph for an arbitrary node 51 57
Solution graph, optimal 60
Solution trees 19 224
SOLVE algorithm 230
SOLVE algorithm with successor ordering 311—317 324—325
SOLVE algorithm, branching factor 263 266—267 317 323 326
SOLVE algorithm, expected complexity 260—267 288 313 323 326 327
SOLVE algorithm, optimality of 264—265
Solving games 230
Somalvico, M. 131
Split-and-prune paradigm 17 19 31 240
Staged search 68 150
Start node 33 74
State 19 21
State-space 20—21 24 26
State-space graphs 21
Static evaluation function 227 334
Status, of game position 224
Stochastically greater 176 199
Stochastically more efficient 177
Stochastically more informed 177 200
Stockman, G. 240 244 273 286 310 325
strategies 12 19
Strategies in games 26 224
Strategies, trees, for representing 19 30 224 240
Strategies, winning 225
Strategy-seeking tasks 12 19 21 26 32
STRIPS 29 119 122 133
Subgoals, auxiliary 29
Subgoals, hierarchy of 28—31 123
Subgoals, independence of 27 121—124
Subproblems 13 222
Subproblems, codes for 22
Subproblems, conjuction of 21 222
Subproblems, interacting 27
Subproportional errors 186—189 193 205 207
Subsets of potential solutions 17 see
Subsets of potential solutions, codes for 17 18 20
Successor nodes 33 74
Successor operator 74
Sum-cost 34 58 74
Symbolic-integration 27 32
Systematic search 4 16 35
Tarsi, M. 31 231 265 266 294
Tentative strategies 36
TEST algorithm 246—247 268
Test tubes 139
Theorem proving 15 20 27 31
Tic-Tac-Toe 117
Tie-breaking rules 81 85 112
Tip nodes 33 64
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте