|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Routh E.J. — A treatise on dynamics of a particle |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Laplace, Other expansions 487 Ex. 3 4 5
Laplace, Series for longitude of a planet, &c 476
Larmor, Calculus of variations 591 note.
Larmor, Inversion 628 note.
Laws, Of Kepler 387
Laws, Of motion 51
Laws, Of resistance 171
Least action, A minimum 647 648
Least action, Case when there is no free path 649
Least action, Parabola, ellipse and any central orbit 651
Least action, principle of 646
Least action, Relation to brachistochrones 650 &c.
Least action, Terms of the second order 653 654
Legendre, Central orbits 356 note.
Legendre, Two centres of force 585 note.
Lejeune Dirichlet, Energy test of stability 296 note.
Lemniscate, A brachistochrone 606 Ex. 5
Lemniscate, Centre of force in the node 320
Lemniscate, The pedal a central orbit 363 Ex. 2
Lemniscate, Time in an arc 201 Ex. 2 3
Lemniscate, Two centres of force, free 587 Ex. 4
Lemniscate, Two centres of force, pressure 190 Ex. 11
Leverrier, True and mean anomalies 347
Limiting velocity, Explained 111
Limiting velocity, Theorems 115 116
Linear equations, Elementary cases 122; see Oscillations.
Linear equations, Theory 118
Liouville, A particle on an ellipsoid 568 note.
Liouville, Solution by Jacobi’s method of a class of problems 645
Liouville, Solution of Lagrange’s equation 522
Liouville, The line arrangement of three attracting particles 406 note.
Liouville, Two centres of force 585 note.
Lloyd and Hadcock, Treatise on Artillery, &c 169 note.
Magnification, Central orbits 369
Magnification, In two dimensions 303
Magnification, Rectilinear motion 139
Mass, Of a planet 403
Mass, Problems on bodies without mass 267
Mass, Units 63
Maxwell, Laws of motion quoted 51
Mayevski, The law of resistance 171
Mean distance, Of a planet, Mean value of 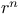 344 344
Miller, Comparison of standards 63
Momentum, angular 79 492
Momentum, Conservation of linear and angular 92
Momentum, Equation of moments in central forces 306
Momentum, Equation of moments in three dimensions 492
Momentum, Equation of moments in two dimensions 259
Momentum, linear 54 79
Moving axes, Geometrical relations between relative and actual path 229
Moving axes, in three dimensions 498
Moving axes, In three dimensions, deduced from Lagrange’s equations 512 Ex. 2
Moving axes, in two dimensions 223
Moving axes, Moving central orbits 359
Moving axes, Moving curves 197
Moving axes, Oblique axes 232
Muirhead, On the laws of motion, referred to 51 note.
Newton, Central forces, a circle 318
Newton, Central forces, a conic about any centre 450
Newton, Central forces, a moving orbit 359
Newton, Constant of gravity 67
Newton, Law of elasticity 83
Newton, Laws of motion 51
Newton, Two attracting spheres 134 Ex. 3
Niven, Motion of projectiles 169 note.
Orbits, A central orbit is a brachistochrone 606
Orbits, Bertrand on closed orbits 428
Orbits, Classification of orbits for 436
Orbits, Orbits at a great distance 438
Orbits, Orbits near the origin 437
Orthogonal Coordinates, Examples and Lamp’s generalization 525
Oscillations, About a steady motion 304
Oscillations, Insufficiency of a first approximation 302
Oscillations, Of a series of  particles 305 particles 305
Oscillations, Of suspended particles 300
Oscillations, One degree of freedom 285
Oscillations, Principal oscillations 292
Oscillations, Problems 138
Oscillations, Small curvilinear 199
Oscillations, Small finite 200
Oscillations, Small rectilinear 137
Oscillations, Two degrees of freedom 287
Oscillations, Use of Lagrange’s equations 513
Painlev , Elimination of time from Lagrange’s equations, page 409 , Elimination of time from Lagrange’s equations, page 409
Painlev , Particle on an ellipsoid 568 note. , Particle on an ellipsoid 568 note.
Parallel forces, Constant see Projectile.
Parallel forces, Variable a conic described 323 452
Parallelogram law, Vectors 222
Parallelogram law, Velocity 4
Parallelogram law, Velocity, acceleration 28
Parallelogram law, Velocity, angular velocity 43
Path, Central forces 309
Path, Laplace’s differential equation 268
Path, Solution in some cases 269 &c.
Pendulum, Change of place 207 &c; see Circle and Conical Pendulum.
Pendulum, Rotation of the earth 621 624
Point to point, A brachistochrone 591
Point to point, Least action 646
Point to point, Path under gravity 159
Point to point, Under a central force 330 339
Poisson, Effect of the rotation of the earth 627
Poisson, Expansion of true anomaly, &c 487 Ex. 3
Pressure, A constrained motion may be free 190 193 194 529
Pressure, Does the particle leave the curve 195
Pressure, Three dimensions 526 &c. 536 552 560
Pressure, Two dimensions 184
Projectiles, Deviation from parabolic motion 623
Projectiles, Given trajectory find the resistance 179
Projectiles, In vacuo 154
Projectiles, In vacuo, by Jacobi’s method 645
Projectiles, Resistance 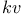 162 162
Projectiles, Resistance 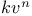 168 168
Projectiles, Resistance 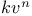 , , 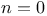 176 Ex. 5 176 Ex. 5
Projectiles, Resistance 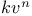 , , 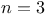 177 177
Projectiles, Resistance 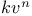 , cases of , cases of 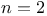 172 172
Projectiles, Rotation of the earth, high and flat trajectories 621
Puisseux, The spirals of 322
Pulleys 78 Ex. 10
Reciprocal spiral, A central orbit 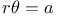 358 358
Reciprocal spiral, Arrival at the centre of force 472
Reciprocal spiral, Radial velocity constant 358
Reich, Experiments at Freiberg 627
Relative motion, Acceleration relative to a moving curve 197
Relative motion, Acceleration relative to a moving point 39 276
Relative motion, Coriolis 257
Relative motion, Relative and actual paths 229
Relative motion, Three dimensions, relative to a moving curve 530
Relative motion, Three dimensions, relative to the meridian plane 495
| Representative particle, Defined 295
Resisting medium, Curvilinear motion of a heavy particle 162 180
Resisting medium, Heavy particle on a chord 107
Resisting medium, Heavy particle on a chord, falls freely 115 &c.
Resisting medium, Law of resistance 171
Resisting medium, Rectilinear motion, light particle 102
Resisting medium, Resistance in the solar system 385
Roberts, R, A, Integral calculus referred to 116
Roberts, W, B, W, Motion on an ellipsoid 568 571
Roger, On brachistochrones 591 note 612
Rouch Convergence in Kepler’s problem 488 Convergence in Kepler’s problem 488
Salmon, Solid geometry referred to 577 610
Sang, Heavy particle on a circle 217
Schiaparelli, Disintegration of comets 414 note.
Second approximations, Central orbits 367 426
Second approximations, Conical Pendulum 562 564
Second approximations, Motion, curvilinear 202 302 303
Second approximations, Rectilinear motion 141
Serret, Lemniscate 201 Ex. 2
Serret, Two centres of force 585 note.
Similar, configurations 265 Ex. 9 10
Similar, Line arrangement of three particles 409 &c.
Similar, Triangle arrangement 407
Singular points, Arrival at the centre of force 468
Singular points, Of infinite force 466
Singular points, Special cases 470 472
Slesser, Acceleration for moving axes 500
Spheres, Energy lost 90
Spheres, Impacts of smooth spheres 83 &c.
Spheres, Impulses of spheres inside moving vessels, tied by strings, &c., examples 94
Spheres, Motion of a point on a sphere 542 &c. 555
Stability, Energy test 296
Stability, Of central orbits 439 444
Stability, Of oscillations 287
Stability, Of the moon’s orbit 417 418
Stability, When the law of force is the inverse  th 298 th 298
Stokes, On the figure of the earth 619 Ex. 5
Stokes, Resistance to comets 386
Stone, Longitude is elliptic motion 476
String 545
String of particles, Initial tensions, &c 279
String of particles.  heavy suspended particles 305 heavy suspended particles 305
String passes over a surface 545
Sufficiency, Insufficiency of a first approximation 302
Sufficiency, Of the equations of motion 243
Superposition, Of motions, Theory 271 275
Surface, About steady motion 553
Surface, Cylinders 544
Surface, developable 549
Surface, Ellipsoid 568
Surface, Motion on any surface 535 &c.
Surface, of revolution 541
Surface, Of revolution, the zones 550 &c Surface Paraboloid
Surface, Small oscillations of a heavy particle about lowest point 301
Surface, sphere 542 555
Swarm, Ellipsoidal swarm, page 406
Swarm, Stability of a spherical swarm 414
Sylvester, Motion in a circle 321
Sylvester, Motion in a circle with two centres of force 194
Tait, Brachistochrone when the velocity varies as the distance from the axis of 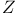 612 Ex. 4 612 Ex. 4
Tait, Least action in elliptic orbits 651
Tait, Relation of brachistochrones to free paths 591 650
Tautochrone, Examples of tautochronous curves 211
Tautochrone, Linear equation 119
Thomson and Tait, Laws of motion 51
Thomson and Tait, Orthogonal surfaces of trajectories 638
Three attracting particles, Initial radius of curvature 284 Ex. 6
Three attracting particles, Line arrangement 409
Three attracting particles, Motion from rest in either arrangement 413 284
Three attracting particles, Stability 408
Three attracting particles, Triangle arrangement 407
Three attracting particles, Unstable 412
Time, Ambiguities in sign 350 353
Time, Ellipse of small eccentricity 345
Time, Euler’s and Lambert’s theorems 350 352
Time, In a central orbit, ellipse 342
Time, In a central orbit, hyperbola 348
Time, In a central orbit, parabola 349
TIME, In an arc 199 200
Tisserand, Comet in a resisting medium 384 &c.
Tisserand, Criterion of the identity of a comet 415
Tisserand, Disintegration 414
Tisserand, Proof of a theorem of Laplace 487 Ex. 4
Tissot, The conical pendulum 555 note.
Todhunter, Error in a Newtonian problem 134 Ex. 3
Todhunter, On brachistochrones 604
Townsend, Memoir on brachistochrones 591 note.
Train and engine 150 Ex. 5 305
Transon, On hyper-acceleration 233
Two attracting particles, Mass of a planet 402
Two attracting particles, Orbit and time 399
Two centres of force, A circle is a possible orbit  194 194
Two centres of force, Ellipse described 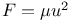 , tree dimensions 529 , tree dimensions 529
Two centres of force, Ellipse described 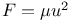 , two dimensions 355 , two dimensions 355
Two centres of force, Liouville’s general solution 585 &c.
Two centres of force, Liouville’s general solution, in three dimensions 588
Two centres of force. 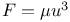 , lemniscate 587 Ex. 4 , lemniscate 587 Ex. 4
Uniform, Angular velocity 41
Uniform, Definition 53
Uniform, Velocity and acceleration 2 15
Units, force 64
Units, Horse-power 72
Units, mass 63
Units, Space and time 46
Units, work 71
Velocity, Components 11
Velocity, In a central orbit from infinity and to the origin 312
Velocity, moment of 6 9
Villarceau, Force in a conic 450 note.
Villarceau, Law of gravitation 390 note.
Vis viva see Energy.
Vis Viva, Constrained particle 184
Vis Viva, Coriolis on relative vis viva 257
Vis Viva, Deduced from Lagrange’s equations 512 Ex. 3
Vis Viva, Defined 69
Vis Viva, Principle for a fixed field 246
Vis Viva, Principle for rotating field 255
Vis Viva, Vis Viva of a rigid body 253
Work, Central force 186
Work, defined 70
Work, Effective forces 507
Work, Elastic string 187
Work, Rate of doing work 72
Work, Work function 185
Worms, Experiments on Foucault’s pendulum 627
Wythoff, Memoir on dynamical stability 406 note.
Young, Rule for the attraction of table land 208
Zenger, Mean and true anomalies 347 Ex. 2
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 particles
particles  , Elimination of time from Lagrange’s equations, page
, Elimination of time from Lagrange’s equations, page 
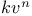
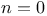
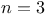
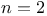
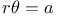
 th
th 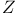

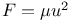 , tree dimensions
, tree dimensions 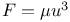 , lemniscate
, lemniscate