јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Collin R.E. Ч Foundations for Microwave Engineerings
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Foundations for Microwave Engineeringsјвтор: Collin R.E. јннотаци€: "FOUNDATIONS FOR MICROWAVE ENGINEERING, Second Edition, covers the major topics of microwave engineering. Its presentation defines the accepted standard for both advanced undergraduate and graduate level courses on microwave engineering. An essential reference book for the practicing microwave engineer, it features:
язык: –убрика: “ехнологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: second edition√од издани€: 2001 оличество страниц: 924ƒобавлена в каталог: 20.02.2006ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Hankel functions 881Ч885 Hankel functions spherical 510Ч511 Harrington, R.F. 63 144 Hartwig, C.P. 156 Harvey, A.P. 479 577 Haskal, H. 224 Haus, H.A. 668 Hayt, W.H., Jr. 70 Heilmeier.G.H. 830 Held, D.N. 875 Helix general properties of 583Ч585 Helix sheath 580Ч583 Helix sheath dispersion equation for 583 Helix sheath in traveling-wave tube 693 HelmholtzТs equation 32 97 HelmholtzТs theorem 19 525 HEMT transistor 722 Hensperger, E.S. 346 Heuer, H.J. 818 Hirshfield, J.L. 712 Homer, J.B. 712 Homo, M. 430 Honey, R.C. 830 Hopfer, S. 207 209 Howe, H. 130 173 Hutter, R.G.E. 576 712 Hybrid junction as balanced mixer 865Ч866 Hybrid junction branch line coupler as 432Ч434 Hybrid junction magic T as 435Ч437 Hybrid junction ring circuit as 437Ч442 Hybrid junction scattering matrix for 436Ч437 441 Image parameters of filters 587Ч590 IMPATT oscillator 837Ч840 Impedance characteristic of capacitively loaded transmission line 556 Impedance characteristic of coaxial line 115 Impedance characteristic of coplanar line 176Ч178 Impedance characteristic of microstrip line 150Ч153 Impedance characteristic of strip line 171 Impedance characteristic of transmission line 76 Impedance general definition of 38 Impedance input, even and odd properties of 232Ч233 Impedance input, on transmission line 93 Impedance inverters in filters 603Ч615 Impedance matching, with lumped elements 319Ч330 Impedance matching, with lumped elements with stubs 309Ч319 (see also УQuarter-wave transformersФ; УTransmission line taperedФ) Impedance matrix imaginary property of 236Ч237 Impedance matrix symmetry of 235Ч236 Impedance mismatch factor 334 Impedance mismatch factor, invariance of 334Ч339 Impedance normalized 90 С237Ч238 Impedance of waveguide elements 339Ч342 Impedance surface 56 Impedance termination, design of 330Ч334 Impedance wave for circular guide 196Ч197 Impedance wave for TE waves in rectangular guide 185 190 Impedance wave for TM waves in rectangular guide 189 Inductance.disributed for transmission line 72Ч73 Inductor, for microsirip circuits 320Ч322 Insertion loss in filters 591Ч592 Interdigital line 577Ч579 Ishii, T.K. 219 Isolator 466Ч468 Ivanek, F. 16 Jackson.R.W. 179 Jahnke, E. 395 James.D.S. 500 Johnk, C.T.A. 70 Johnson noise 762 Johnson, R.C 393 Jones, E.M.T. 364 434 830 Kajfez, D. 549 Kales, M.L. 465 Kaul, R. 210 Kerns, D.M. 302 Kerr, A.R. 875 Kinetic power theorem for electron beam 670 Kinetic voltage 670 Kleen, W.J. 712 Klopenstein, R.W. 393 Kluever, J.W. 668 Klystron reflex electronic admittance in 6B6 Klystron reflex oscillation conditions for 688 Klystron reflex tuning curves for 688Ч689 Klystron reflex two-cavity 678Ч686 Klystron reflex two-cavity equivalent circuit for 684Ч685 Klystron reflex two-cavity excitation of fields in 683Ч686 Klystron reflex two-cavity gain of 685 Knight, S.P. 322 Knipp, J.K. 712 Knoppik, N. 497 499 Kobayshi, M. 162 Kollberg, E.L. 875 Komatsu, Y. 515 Kong, J.A. 70 149 Kotzebue, K.L. 830 Kratis, J.D. 16 70 Krauss, H.L. 712 Kuhn, N. 264 Kurokawa, K. 268 549 Lange, J. 434 LaplaceТs equation 29 Larmor frequency 452 Laverghetta, T. 130 Lax, B. 480 Lewin, L. 340 342 902 Lewis, J. 712 Li, Q.F. 712 Liboff.R.L. 219 Liechti, C.H. 717 Lorentz condition 57 133 Lorentz force 17Ч18 Lorentz reciprocity theorem 62Ч64 Loss tangent 26 Magic T 435Ч437 865Ч868 Magnetic permeability 13 27 Magnetic permeability for ferrite 455 457Ч459 magnetic susceptibility 27 Magnetron 690Ч692 Makimoti, M. 647 Malherbe, J.A.G. 647 Manley, J.M. 804 Manley-Rowe relations 804Ч807 Marcuvitz, N. 207 302 339Ч340 479 552 Mason, S.J. 261 Mass, S.A. 875 Masse, D.J. 156 Matching network design of for amplifier 330Ч334 338Ч339 Matching network lumped element 319Ч330 Matching network lumped element Q of 325Ч330 Matching network lumped element with transmission line stubs 309Ч3 Matsumaru, K. 393 Matthaei, G.L. 364 434 630 830 Matthews, H. 647 MaxwellТs equations 21 McDonald, N.A 286 McLachlan, N.W. 885 Meander line 577Ч579 Medina, V. 430 Meixner, J. 43 Melchor, J.L. 456 MESFET 721 MIC circuit 714 Microstrip line 125Ч128 130Ч169 Microstrip line, attenuation of 153Ч157 163Ч164 Microstrip line, coupled 164Ч170 Microstrip line, dispersion in 158Ч11 Microstrip line, effective dielectric constant for 149Ч152 Microstrip line, impedance of 150Ч153 Microstrip line, inverted-suspended 126Ч127 Microstrip resonator 490Ч496 Microstrip resonator, disk 496Ч500 Microstrip resonator, disk Q of 499 Mihran, T.G. 660 Mixer 856Ч868 Mixer, balanced 865Ч868 Mixer, compression in 862Ч863 Mixer, harmonic balance method for 869Ч873 Mixer, image-enhanced 868 Mixer, image-rejection 868 Mixer, intermodulation in 863Ч864 Mixer, noise figure 864Ч865 Mixer, subharmonic 868 MMIC circuits 714 Mobbs.C.I. 647 Mode chart for cylindrical cavity 507 Montgomery, C.G. 16 220 245 302 416 479 548 Moore, R.K. 16 Morich, M. 166 Moynihan, R.L. 449 Mumford, W.W. 636 Murakami, Y. 515 N-port circuits 233Ч235 Nakatani, A. 180 Naldi, C U. 176 Negative-resistance amplifier 814-S21 Nelson, J. 500 Noise, conductance equivalent 767 Noise, conductance equivalent temperature of 762 Noise, conductance figure 768Ч773 Noise, conductance figure circles for 772Ч776 Noise, conductance figure of cascaded stages 770Ч772 Noise, conductance figure of mixer 664Ч865 Noise, conductance figure of parametric amplifier 821Ч829 Noise, conductance figure optimum source impedance for minimum 769Ч770 Noise, conductance in two-parts 766Ч767 Noise, conductance Johnson or Nyquist 762 Noise, conductance resistance, equivalent 767 Noise, conductance temperature of amplifier 771 Noise, conductance temperature of system 771Ч772 Noise, conductance theory of 760Ч765 Normalised load impedance 90 Normalized current 223 Normalized voltage 223 O-type traveling-wave tube 692Ч699 Okress, E.C 16 Ordung, P.F. 712 Oscillators Gunn 832Ч837 Oscillators IMPATT diode 837Ч840 Oscillators three-port scattering matrix for 843Ч849 Oscillators transistor 840Ч856 Oscillators, design of 851Ч856 p-n junction diode 800Ч802 Pannenborg, A.E. 302 Parad, L.L 449 Parallel plate transmission line 117Ч125 Parametric amplifier linearized equations for 807Ч809 Parametric amplifier Manley Ч Rowe relations for 804Ч807 Parametric amplifier negative resistance 814Ч821 Parametric amplifier negative resistance gain of 815Ч820 Parametric amplifier negative resistance gain-bandwidth product far 821 Parametric amplifier negative resistance noise in 823Ч825 Parametric amplifier noise figure of degenerate negative resistance 825Ч829 Parametric amplifier noise figure of negative resistance 823Ч825 Parametric amplifier noise figure of up-converter 821Ч823 Parametric amplifier p-n junction diodes for 800Ч802 Parametric amplifier up-converter 809Ч814 Parametric amplifier up-converter gain of 813 Park, S.Y. 712 Pavio, A.M. 719 798 875 Penfield, P. 830 Pengelley, R.S. 722 798 Periodic structures and filters 587Ч590 Periodic structures for traveling-wave tube helix, general properties of 583Ч585 Periodic structures for traveling-wave tube interdigitai line 577Ч579 Periodic structures for traveling-wave tube meander line 577Ч579 Periodic structures for traveling-wave tube sheath helix 580Ч583 Periodic structures for traveling-wave tube tape ladder line 577Ч578 Periodic structures for traveling-wave tube, corrugated plane 571Ч577 Periodic structures unsymmetrical two-ports in 559Ч560 Periodic structures, 564Ч566 Periodic structures, Bloch waves in 556 Periodic structures, Bloch-wave impedance for 555Ч556 Periodic structures, energy flow velocity in 566Ч571 Periodic structures, FloquetТs theorem for 569Ч57] Periodic structures, group velocity in 566Ч571 Periodic structures, matching of 563Ч564 Periodic structures, spatial harmonics in 569Ч571 Periodic structures, terminated 560Ч563 Permeability 18 27 Permeability for ferrite 455 457Ч459 Perveance of electron heam 650 Phase shifter, electronnic 409Ч413 Phase shifter, rotary 404Ч409 phase velocity 47 198Ч199 Phase velocity in waveguides 182 Physical constants 911Ч912 Pierce, J.R. 650 653 712 Pierpont, J. 229 PIN diode 401Ч403 Plane waves 44Ч48 Plasma frequency 653 Plasma frequency effective 659 Poh, S.Y. 149 PoissonТs equation 29 Polarization circular 405Ч407 452 Polarization in dielectric 23Ч27 Polarization of circular aperture 285 Post capacitive in waveguide 342 Post inductive, in waveguide 341 Potential scalar, dynamic 57 Potential scalar, static 28 Potential vector, dynamic 57 Potential vector, static 30 Power added efficiency 842 Power divider 442Ч450 Power divider Wilkinson 443Ч450 Power for TE waves in rectangular guide 186 187 Power gain 274 728Ч735 Power loss ratio in filter 591Ч594 Power loss ratio in quarter-wave transformer 356Ч357 Power orthogonality in waveguides 185 Power waves, scattering matrix for 268Ч276 Power, in circular guide 197 Poynting vector 38Ч39 Poynting vector complex 37 Pozar, D.M. 219 479 Pratt, T. 16 Presser, A. 434 Probe, radiation resistance of, in waveguide 281 Pucel, R.A. 156 Pulse propagation on transmission line 78Ч85 Purcell, E.M. 220 245 302 416 479 548 Quality factor or Q 325 503Ч504 Quality factor or Q external 483 Quality factor or Q loaded 483 Quality factor or Q of cylindrical cavity 507 Quality factor or Q of dielectric resonator 513 Quality factor or Q of disk resonator 499 Quality factor or Q of matching network 325Ч330 Quality factor or Q of rectangular cavity 503Ч504 Quality factor or Q unloaded 483 Quarter-wave plate 405 Quarter-wave transformers Chebyshev, exact results 356Ч360 Quarter-wave transformers Chebyshev, three-section 359Ч360 Quarter-wave transformers Chebyshev, two-section 356Ч358 Quarter-wave transformers N-section binomial 350Ч352 Quarter-wave transformers N-section Chebyshev 352Ч356 Quarter-wave transformers N-section, approximate theory for 348Ч350 Quarter-wave transformers prototype circuit for filter 360Ч370 Quarter-wave transformers single-section 343Ч346
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



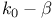 diagram for
diagram for