|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Mandl F., Shaw G. — Quantum field theory |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
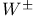 boson 237 272 boson 237 272
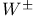 boson, decay 254 boson, decay 254
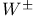 boson, mass 239 301—302 boson, mass 239 301—302
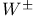 boson, production 239 322 boson, production 239 322
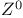 boson 257 272 boson 257 272
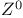 boson, decay 318 321 325 326 boson, decay 318 321 325 326
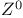 boson, mass 258 301—302 boson, mass 258 301—302
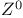 boson, production 257 317—321 boson, production 257 317—321
't Hooft gauge 288
Abelian 265
absorption operator 8 62 68 87
Adiabatic hypothesis 102 192
Angular momentum, conservation 37—40
Angular momentum, of a spinor field 65
Annihilation operator 8 45 see
Anti-particle 49—50 70—71
Bare particle 102 117 176
Basic vertex part 108
Bhabha scattering 116 150
Bilinear covariants 335 339
Bloch — Nordsieck theorem 170 171
Bose — Einstein statistics 9 72—73
Branching ratio 246
Bremsstrahlung 165
Canonical quantization 30—33
Charge, conjugation 58 94
Charge, conservation 36
Charge, operator 36 49 65 69
Charge, renormalization 186 191 194 196—198 213 214
Chiral phase transformations 80
Coherent photon states 10 25
Commutation relations, canonical 32
Commutation relations, covariant 50
Commutation relations, equal-time 33
Compton scattering 122 153 180
Conjugate field 31
Conservation laws, angular momentum 37—40
Conservation laws, derivation from symmetries 33
Conservation laws, electric charge 36 49 262
Conservation laws, energy-momentum 37—40
Conservation laws, lepton numbers 132 240 294
Continuity equation 34
Contraction, identities of gamma matrices 329
Contraction, of field operators 104
Coulomb gauge 3
Coulomb scattering 162
Coulomb scattering, electron polarization in 163
Counterterm 190 213
Covariant derivative 263 269 270 290
Creation operator 8 45 62 68 87
Cross-section, general formula for 138
Current, charged 257 266
Current, conserved 35 82 92 262
Current, electromagnetic 49 65 266
Current, leptonic 237 266
Current, neutral 257 266 272
Current, weak, hypercharge 267
Current, weak, isospin 266
Decay of 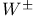 boson 254 boson 254
Decay of 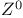 boson 318 321 325 326 boson 318 321 325 326
Decay of Higgs particle 325
Decay of muon 247 259
Decay of tauon 253
Decay rates, general formula for 245
Decay width 246
Destruction operator see “Absorption operator”
Dimensional regularization 222 226
Dirac equation 63 327
Dirac equation, gamma matrices 327
Dirac equation, gamma matrices, anticommutation relations 328
Dirac equation, gamma matrices, contraction identities 329
Dirac equation, gamma matrices, Dirac — Pauli representation 336
Dirac equation, gamma matrices, Majorana representation 70 338
Dirac equation, gamma matrices, trace theorems 329
Dirac equation, plane wave solutions 331
Dirac equation, projection operators, energy 332
Dirac equation, projection operators, helicity 333
Dirac equation, projection operators, spin 334
Dirac equation, relativistic properties 334 339
Dirac equation, spin, matrices 328
Dirac equation, spin, operator 70
Dirac equation, spin, summations 141
Electric dipole approximation 10 19
Electro-weak theory see “Standard electro-weak theory”
Electron-electron scattering 113 125 173
Electron-muon scattering 172
Electron-positron annihilation, 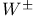 pair production 322 pair production 322
Electron-positron annihilation, 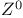 production 317—321 production 317—321
Electron-positron annihilation, Higgs particle production 323—325
Electron-positron annihilation, lepton pair production 146 315—320
Electron-positron annihilation, lepton pair production, asymmetry in 317
Electron-positron scattering 116 150
Electron-proton scattering 172
Energy projection operators 332
Energy-momentum conservation 37—40
External, field 159
External, line 76
Fermi coupling constant 248 252 349
Fermi — Dirac statistics 63 72—73
Feynman amplitude 122 129
Feynman amplitude, and gauge invariance 144—145 173
Feynman diagram 55 74—77 Chap.
Feynman diagram, irreducible 215
Feynman diagram, primitively divergent 216
Feynman diagram, proper 212
Feynman diagram, skeleton 215
Feynman gauge 303
Feynman parameter 223
Feynman rules see “Appendix B”
Feynman rules, external field 162
Feynman rules, intermediate vector boson theory 244
Feynman rules, QED 128
Feynman rules, standard electro-weak theory 303
Fierz identities 313
Form factor 172
Furry's theorem 182
Gamma matrices see “Dirac equation”
Gauge, bosons 272
Gauge, bosons, self-interaction 274 305 308—311
Gauge, field 263 269 270
Gauge, fixing term 288
Gauge, transformations, electromagnetic 3 78—79 84 262 291
Gauge, transformations, of the first kind 36
Gauge, transformations, of the second kind 3
Gauge, transformations, SU(2) 268—269 290
Gauge, transformations, U(1) 270 290
Gauge, transformations, weak hypercharge 270 290
Ghost particle 289
Glashow model 275
Goldstone boson 284
Goldstone model 280
Gordon identity 339
Gupta — Bleuler formalism 87—90
Heisenberg picture 22—24
Helicity, projection operators 333
Helicity, states 70
Higgs, field 289 298
Higgs, mechanism 287
| Higgs, model 284
Higgs, particle 287 301 322
Higgs, particle, decay 325
Higgs, particle, mass 302—303
Higgs, production and detection 322—325
Higgs, propagator 304
Hypercharge see “Weak hypercharge”
I amb shift 203
Indefinite metric 90
Infra-red divergence 167 168 208
Interaction picture 22—24
Inverse muon decay 253 259
Isospin see “Weak isospin”
IVB theory 236
Klein Nishina formula 159
Klein — Gordon equation 43
Left- and right-handed spinor fields 241 264
Lepton number conservation 132—133 240 294
Life-time 14 246
Lorcntz transformation of Dirac spinors 335
Lorentz condition 84
Lorentz gauge 84
Magnetic moment, of electron 200—203 231
Magnetic moment, of muon 202—203
Majorana representation 70 338
Metric tensor 28
Microcausality 52 73 79 80
Minimal substitution 77 94
Mixed T-product 104
Mott scattering 162 172 173
Muller scattering 113 125 173
Muon, decay 247 259
Muon, magnetic moment 202—203
Neutrino electron scattering 253 255 259 311
Neutrino, masses 240 293 300
Neutrino, mixing 293 326
Neutrino, oscillations 294
Noetther's theorem 35
Non-abelian 265
Normal product 46 69 103 105
Number representation 9 48 61
Pair annihilation see “Electron-positron annihilation”
Parity, transformation 59
Parity, violation 241 259
Pauli exclusion principle 115
Phase transformations, global 36
Phase transformations, local 79
Photon, mass 183 185
Photon, polarization vectors 5 9 85—86
Photon, self-energy 118 182 213 229
Polarization calculations for electrons 143 163
Polarization calculations for photons 21 26 157—159
Polarization summations for fermions 141
Polarization summations for photons 144
Polarization vectors for massive vector bosons 243
Polarization vectors for photons 5 9 85—86
Positive and negative frequency parts 10
Primitive divergence 216
Proca equation 242
Projection operators see “Dirac equation”
Propagator, fermion 73
Propagator, massive scalar boson 304
Propagator, massive vector boson 243
Propagator, meson 53
Propagator, photon 86 90
Quarks 294
Radiation gauge 3
Radiative corrections 170 Chap.
Radiative corrections, higher-order 211
Radiative corrections, Lamb shift 203
Radiative corrections, lowest-order 198
Radiative corrections, magnetic moments 200
Radiative corrections, soft photons 170 208—211 317
Radiative corrections, standard electro-weak theory 302
Reduction 215
Regularization 175
Regularization, cut-off procedure 183 198—199 225
Regularization, dimensional 222 226
Rehormalization, charge 186 191 194 196—198 213 214
Rehormalization, constants 186 191 196 198 213 214 234
Rehormalization, external line 192 214
Rehormalization, mass 188—191 213 225 234
Rehormalization, of fermion propagator 191 213
Rehormalization, of photon propagator 186 213
Renormalizability 218
Renormalizability, dimensional criterion for 217 259
Renormalizability, of Higgs model 287
Renormalizability, of Higgs model, IVB theory 258
Renormalizability, of Higgs model, QED 211—219
Renormalizability, of Higgs model, standard electro-weak theory 294
Rosenbluth formula 172
Rutherford scattering 163
S-matrix expansion 98
Scattering by an external field 159 200 208—210 233
Schroedinger picture 22—24
Self-energy, electron 117 127 187 211—213 225 234
Self-energy, photon 118 182 213 229
Spin, and statistics 72—73
Spin, operator 70
Spin, projection operators 334
Spin, summations 141
Spontaneous emission 14
Spontaneous symmetry. breaking 280 Chap.
Standard electro-weak theory 289 Chap.
Standard electro-weak theory, boson masses 300—302
Standard electro-weak theory, Feynman rules 303 344
Standard electro-weak theory, interactions 301 305
Standard electro-weak theory, Lagrangian density 295 300
Standard electro-weak theory, lepton masses 292 300
Standard electro-weak theory, renormalizability 294 303
SU(2) transformations 265 268—269 290
T-product see “Time-ordered product”
Tauon, decay 253
Tauon, mass 149
Thomson scattering 20 26 157
Time-ordered product 53 74 101 104
Trace theorems 329
U(1) transformations 268 270 290 291
Unitary gauge 286 298
Units, electromagnetic 2
Units, natural 96
Units, natural, dimensions of fields in 97
Universality 131 253
V-A interaction 240
Vacuum, diagram 119
Vacuum, polarization 118 207—208 229
Vacuum, state, definition 9 46 68 87
Vacuum, state, degeneracy of 280 291
Vertex, modification 194 214
Vertex, part 108
Ward identity 197 234
Wave function renormalization 194
Weak hypercharge 267
Weak isospin 265—267 274
Weak mixing angle 271
Weinberg angle 271
Weyl field 80
Wick's theorem 102
Yukawa interaction 292
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



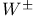 boson
boson 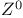 boson
boson